We all have these gigabytes and terabytes of hard disks in our computers. But what's the use of this huge storage if we cannot see where our files are and in which folder they are located? Of course we can. With our very own IDE, Lazarus!
There are many file managers out there. Ther's a file manager made with Lazarus which is being served in the internet, named Double commander. And I am sure there are many others made with Lazarus. But as a programer you would want a file manager of your own, right? The one with fancy stuff that you care about and design the interface you always like. That's when this may help you.
If you are interested in ready made component that list the files in a directory then you can use TShellListView under the Others tab in the top toolbar. You can also use this tutorial to create a File Browser in 2 mintues! But its not that much customizable.
Start Lazarus.
Create a new Program Project (Project-> New Project-> Program-> OK).
Now paste the following code:
The above code has been polished from the code available here.
Now Run the project (F9 or Run->Run).
If you haven't saved the project yet, then the project is temporarily saved in the temp directory of your Operating System. The program will be listing the files in the temp directory.
Explanation:
Now we go through what we have done to get the program to work.
Info is a TSearchRec or in human terms it is a search record which can hold the file names and their info in it. When we will search the files inside a folder/directory it will have all the information of the files:
Then...
Count is for holding the file count.
We haven't found a file yet. So we assume that we have 0 files.
We try to find the file that is in the folder. To find the first file we have to use FindFirst. It has the following syntax:
We see the parameters one by one:
(1) When we use FindFirst we have to specify a pattern, which also works with a path. For example, if we wanted to list all the text files in a directory, we could set it to '*.txt'. In our example code we want all files so we used '*' as a pattern. We can also use, for example, 'C:\Windows\*.bmp', which will list all the .bmp bitmap files inside the C:\Windows\ directory.
(2) Attr is the type of the file we want. We want files and directories so we used "faAnyFile and faDirectory". You may use other constants as well:
(3) The Rslt is the TSearchRec that will have the file info of the first item (not all of them). To get the rest of the items one by one, we would need to use FindNext.
We repeat until the FindNext function returns 0 (zero). It will return 0 when there are no more files to list. So it will get the file information in the Info TSearchRec every time there is an item. We increase the Count variable each time we get a new file.
We have used with...do statement here so that we don't have to write Info everytime we use something from the Info. (Like: Info.Name, Info.Size, Info.Attr...) We list all the "Name"s and "Size"s. When we have a directory, we would just add a prefix 'Dir : ' before the name. That's it. Its not that hard, is it?
Start Lazarus.
Create a new Application Project (Project-> New Project-> Application-> OK).
Drop a TDirectoryEdit from Misc tab and also drop a TListBox from the Standard tab in the form.
Now switch to Code view (F12) and enter the following procedure after the "{$R *.lfm}" line:
Now move your cursor on the procedure name then press Ctrl+Shift+C to declare it at the top. The procedure is useless if you don't declare it.
Double Click the TDirectoryEdit and enter:
Now Run the project (F9 or Run-> Run). Now open some directory and you will see the list in the List box.
It is a very basic example. You can use TListview to show file name, size and modified date etc. I have made such a project for you. It is available from the download at the end of the post. In our 2 minute File Browser example, we don't actually get the file list in our code. All the file list viewing is done with communicating between the components. But if we use FindFirst, FindNext, FindClose method, we really get the file names. We can do many things with it. We can only show the jpg files in a folder. We can also draw the image thumbnails in a TPaintbox to emulate a really cool image thumbnail app.
The form layout is as follows:
The components are:
And a screenshot of it on runtime:
The above one is very much of understandable interface. While the first one is pretty much elementary. So it is better to choose to show files in a TListView. You can show your own icons for the folders and files.
So what I have done is I have dropped a TListView and made 3 columns (by clicking [...] button in Columns property and then setting its Caption and Width with the Object Inspector). I have dropped a TShellTreeView to show the drives in a tree.
I have a ShowDirectory procedure like below:
We use the FindFirstUTF8, FindNextUTF8 and FindCloseUTF8 functions. What's the reason? If we have some file name which is written in unicode characters then using FindFirst etc. will not render it correctly, because they don't support UTF-8. FindFirstUTF8 on the other hand does. So we use it for better compatibility.
We have access to the file size information, but it is in bytes. Can you understand how many megabytes a file is when it is of 2621440 bytes? It is actually awkward for the user to see the file size in bytes all the time. So we have to convert the file size information to get an expected output:
For the file modified date and time we use the following code (in the ShowDirectory procedure mentioned above):
li is the TListItem we will add. You can change the date format. Get some help here about the date and time formatting.
We also have to go inside a folder when the user double clicks a folder in the TListView. And we also need to run a file with the default program when the user double clicks a file name. So we add this to the OnDoubleClick event of TListView:
The wiki suggests to use TProcess instead of Shell Execute. Because this command will only work on windows. TProcess on the other hand works on all platforms.
Or here: http://bit.ly/18cGsOG
Size: 562 KB
The package contains compiled executable EXE.
There are many file managers out there. Ther's a file manager made with Lazarus which is being served in the internet, named Double commander. And I am sure there are many others made with Lazarus. But as a programer you would want a file manager of your own, right? The one with fancy stuff that you care about and design the interface you always like. That's when this may help you.
If you are interested in ready made component that list the files in a directory then you can use TShellListView under the Others tab in the top toolbar. You can also use this tutorial to create a File Browser in 2 mintues! But its not that much customizable.
Fun in Console!
We would create a file manager in a minute. But first you can try the file listing code in the console. The basics are pretty same, but you can have a clear idea of how it can be done.Start Lazarus.
Create a new Program Project (Project-> New Project-> Program-> OK).
Now paste the following code:
program ListFiles;
{$mode objfpc}{$H+}
uses
{$IFDEF UNIX}{$IFDEF UseCThreads}
cthreads,
{$ENDIF}{$ENDIF}
Classes, sysutils
{ you can add units after this };
var
Info : TSearchRec;
Count : Longint;
begin
Count:=0;
// if we have found a file...
If FindFirst ('*',faAnyFile and faDirectory,Info)=0 then
begin
repeat
// we increase the count so that we can show it later
Inc(Count);
// we do stuff with the file entry we found
with Info do
begin
If (Attr and faDirectory) = faDirectory then
Write('Dir : ');
Writeln (Name:40,Size:15);
end;
until FindNext(info)<>0;
end;
// we are done with file list
FindClose(Info);
Writeln ('Finished search. Found ',Count,' matches');
ReadLn;
end.
The above code has been polished from the code available here.
Now Run the project (F9 or Run->Run).
If you haven't saved the project yet, then the project is temporarily saved in the temp directory of your Operating System. The program will be listing the files in the temp directory.
Explanation:
Now we go through what we have done to get the program to work.
var Info : TSearchRec;
Info is a TSearchRec or in human terms it is a search record which can hold the file names and their info in it. When we will search the files inside a folder/directory it will have all the information of the files:
type TSearchRec = record Time: LongInt; //Timestamp of the file. Size: Int64; //Size of the file. Attr: LongInt; //Attributes of the file. Name: TFilename; //File name (no directory part) ExcludeAttr: LongInt; //Attributes to exclude from search (do not use). FindHandle: Pointer; //Internal OS handle (do not use). Mode: TMode; //Unix File mode. Only used on Unix systems. PathOnly: AnsiString; //Path component of the file end;
Then...
Count : Longint;
Count is for holding the file count.
begin Count:=0;
We haven't found a file yet. So we assume that we have 0 files.
If FindFirst('*',faAnyFile and faDirectory,Info)=0 then
We try to find the file that is in the folder. To find the first file we have to use FindFirst. It has the following syntax:
function FindFirst( const Path: ; Attr: LongInt; out Rslt: TSearchRec ):LongInt;
We see the parameters one by one:
(1) When we use FindFirst we have to specify a pattern, which also works with a path. For example, if we wanted to list all the text files in a directory, we could set it to '*.txt'. In our example code we want all files so we used '*' as a pattern. We can also use, for example, 'C:\Windows\*.bmp', which will list all the .bmp bitmap files inside the C:\Windows\ directory.
(2) Attr is the type of the file we want. We want files and directories so we used "faAnyFile and faDirectory". You may use other constants as well:
faReadOnly: The file is read-only. faHidden: The file is hidden. (On unix, this means that the filename starts with a dot) faSysFile: The file is a system file (On unix, this means that the file is a character, block or FIFO file). faVolumeId: Drive volume Label. Not possible under unix, and on Windows-like systems, this works only for plan FAT (not Fat32 of VFAT) filesystems. faDirectory: File is a directory. faArchive: file needs to be archived. Not possible on Unix
(3) The Rslt is the TSearchRec that will have the file info of the first item (not all of them). To get the rest of the items one by one, we would need to use FindNext.
repeat // we increase the count so that we can show it later Inc(Count); //... //... until FindNext(info)<>0;
We repeat until the FindNext function returns 0 (zero). It will return 0 when there are no more files to list. So it will get the file information in the Info TSearchRec every time there is an item. We increase the Count variable each time we get a new file.
// we do stuff with the file entry we found
with Info do
begin
If (Attr and faDirectory) = faDirectory then
Write('Dir : ');
Writeln (Name:40,Size:15);
end;
We have used with...do statement here so that we don't have to write Info everytime we use something from the Info. (Like: Info.Name, Info.Size, Info.Attr...) We list all the "Name"s and "Size"s. When we have a directory, we would just add a prefix 'Dir : ' before the name. That's it. Its not that hard, is it?
The Graphical Way...
Start Lazarus.
Create a new Application Project (Project-> New Project-> Application-> OK).
Drop a TDirectoryEdit from Misc tab and also drop a TListBox from the Standard tab in the form.
Now switch to Code view (F12) and enter the following procedure after the "{$R *.lfm}" line:
procedure TForm1.ShowDirectory(ListDir:string);
var
Info : TSearchRec;
Count : Longint;
begin
Count:=0;
ListBox1.Clear;
// if we have found a file...
If FindFirst (ListDir+'*',faAnyFile and faDirectory,Info)=0 then
begin
repeat
// we increase the count so that we can show it later
Inc(Count);
// we do stuff with the file entry we found
with Info do
begin
// If we find a folder
if (Attr and faDirectory) <> 0 then
ListBox1.Items.Add('[ '+Name+' ]')
// if we find a file
else
ListBox1.Items.Add(Name);
end;
until FindNext(info)<>0;
end;
// we are done with file list
FindClose(Info);
Caption:=inttostr(Count);
end;
Now move your cursor on the procedure name then press Ctrl+Shift+C to declare it at the top. The procedure is useless if you don't declare it.
Double Click the TDirectoryEdit and enter:
procedure TForm1.DirectoryEdit1Change(Sender: TObject); begin ShowDirectory(DirectoryEdit1.Directory+'\'); end;
Now Run the project (F9 or Run-> Run). Now open some directory and you will see the list in the List box.
It is a very basic example. You can use TListview to show file name, size and modified date etc. I have made such a project for you. It is available from the download at the end of the post. In our 2 minute File Browser example, we don't actually get the file list in our code. All the file list viewing is done with communicating between the components. But if we use FindFirst, FindNext, FindClose method, we really get the file names. We can do many things with it. We can only show the jpg files in a folder. We can also draw the image thumbnails in a TPaintbox to emulate a really cool image thumbnail app.
The form layout is as follows:
The components are:
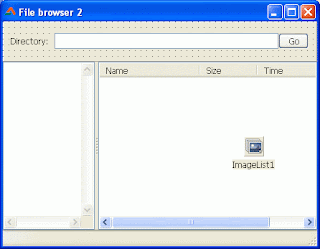
And a screenshot of it on runtime:
The above one is very much of understandable interface. While the first one is pretty much elementary. So it is better to choose to show files in a TListView. You can show your own icons for the folders and files.
So what I have done is I have dropped a TListView and made 3 columns (by clicking [...] button in Columns property and then setting its Caption and Width with the Object Inspector). I have dropped a TShellTreeView to show the drives in a tree.
I have a ShowDirectory procedure like below:
procedure TForm1.ShowDirectory(ListDir:string);
var
Info: TSearchRec;
Count: Longint;
li: TListItem;
FileTime: TDateTime;
begin
ListDir:=AddBackSlash(ListDir);
edtPath.Text:=ListDir;
CurrentDirectory:=ListDir;
Count:=0;
FileList.Items.Clear;
FileList.Items.BeginUpdate;
// This is a try block which finally runs EndUpdate
try
// if we have found a file...
If FindFirstUTF8 (ListDir+'*',faAnyFile and faDirectory,Info)=0 then
begin
repeat
// we increase the count so that we can show it later
Inc(Count);
// we do stuff with the file entry we found
with Info do
begin
if (Name <> '.') and (Name <> '..') then begin
li := FileList.Items.Add;
li.Caption:=Info.Name;
// If we find a folder
if (Attr and faDirectory) <> 0 then begin
li.ImageIndex:=1;
li.SubItems.Add('--'); // folders can't show size
end
// if we find a file
else begin
li.ImageIndex:=2;
li.SubItems.Add(FileSizeFormat(Info.Size));
end;
FileTime := FileDateToDateTime(Info.Time);
li.SubItems.Add(FormatDateTime('dd mmm yyyy hh:nn am/pm',FileTime));
// for help with the format:
// http://lazarus-ccr.sourceforge.net/docs/rtl/sysutils/formatchars.html
end;
end;
until FindNextUTF8(info)<>0;
end;
finally
FileList.Items.EndUpdate;
end;
// we are done with file list
FindCloseUTF8(Info);
StatusBar.SimpleText:=inttostr(Count)+' items';
end;
We use the FindFirstUTF8, FindNextUTF8 and FindCloseUTF8 functions. What's the reason? If we have some file name which is written in unicode characters then using FindFirst etc. will not render it correctly, because they don't support UTF-8. FindFirstUTF8 on the other hand does. So we use it for better compatibility.
We have access to the file size information, but it is in bytes. Can you understand how many megabytes a file is when it is of 2621440 bytes? It is actually awkward for the user to see the file size in bytes all the time. So we have to convert the file size information to get an expected output:
function TForm1.FileSizeFormat(bytes:Double):string;
begin
// below 1024 bytes
if bytes < 1024 then
Result:=floattostr(bytes) + 'b'
// kilobytes; 1kb = 1024bytes
else if (bytes >= 1024) and (bytes < 1024*1024) then
Result:=FormatFloat('0.00', bytes/1024)+'kb'
// megabytes; 1mb = 1024*1024bytes
else if (bytes >= 1024*1024) and (bytes < 1024*1024*1024) then
Result:=FormatFloat('0.00', bytes/1024/1024)+'mb'
// gigabytes; 1gb = 1024*1024*1024bytes
else if (bytes >= 1024*1024*1024) and (bytes < 1024*1024*1024*1024) then
Result:=FormatFloat('0.00', bytes/1024/1024/1024)+'gb'
// for everything above, we show it in terrabytes
else
Result:=FormatFloat('0.00', bytes/1024/1024/1024/1024)+'tb';
end;
For the file modified date and time we use the following code (in the ShowDirectory procedure mentioned above):
FileTime := FileDateToDateTime(Info.Time);
li.SubItems.Add(FormatDateTime('dd mmm yyyy hh:nn am/pm',FileTime));
li is the TListItem we will add. You can change the date format. Get some help here about the date and time formatting.
We also have to go inside a folder when the user double clicks a folder in the TListView. And we also need to run a file with the default program when the user double clicks a file name. So we add this to the OnDoubleClick event of TListView:
procedure TForm1.FileListDblClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
if FileList.Selected.ImageIndex = 1 then
ShowDirectory(AddBackSlash(AddBackSlash(CurrentDirectory)+FileList.Selected.Caption))
else
ShellExecute(Form1.Handle, PChar('open'),
PChar(AddBackSlash(CurrentDirectory)+FileList.Selected.Caption),
PChar(''), PChar(''), 1);
end;
The wiki suggests to use TProcess instead of Shell Execute. Because this command will only work on windows. TProcess on the other hand works on all platforms.
Download Sample Code ZIP
You can download the above example tutorial project source code from hereOr here: http://bit.ly/18cGsOG
Size: 562 KB
The package contains compiled executable EXE.